Overview: Whiplash
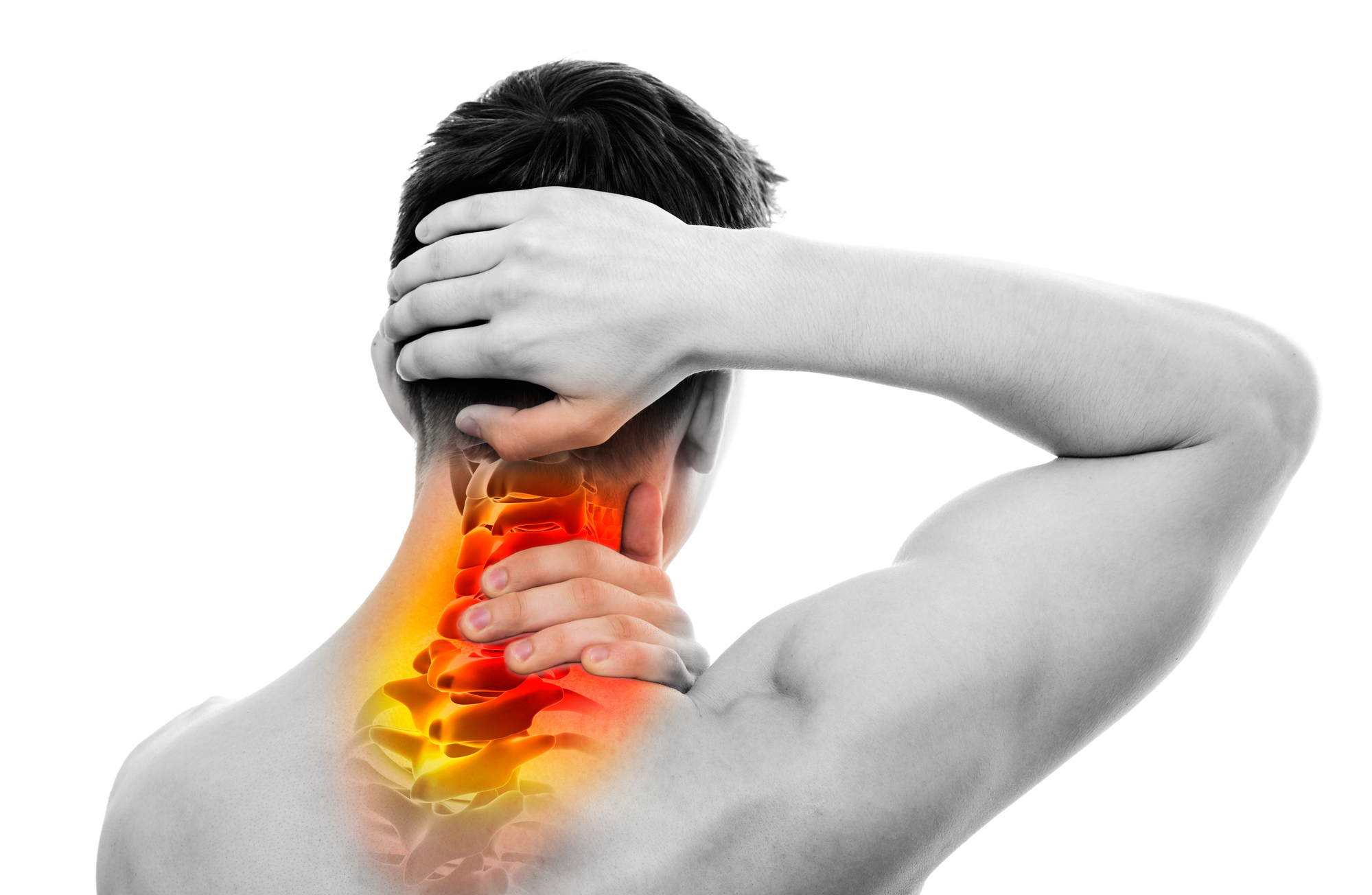
Whiplash is a neck injury resulting from a sudden, forceful impact that causes the head to snap back and forth, similar to the motion of a whip. This type of trauma is commonly associated with car accidents, but can also occur from sports injuries or falls. Symptoms typically include neck pain, stiffness, headaches, and in some cases, pain or numbness in the shoulders, arms, or upper back. The injury occurs when the soft tissues of the neck, including muscles, ligaments, and tendons, are stretched or torn. Diagnosis is generally based on a medical history and physical examination, with imaging tests used to rule out fractures or other complications. Treatment usually involves rest, pain management with medications, physical therapy, and exercises to restore mobility and strength. Most individuals recover fully with appropriate care.
